Alopecia Areata Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Evidence Based
All the information in this blog post is accurate, trustworthy, scientifically based and has been written and fact-checked by our experts and doctors.
Our licensed nutritionists and dietitians are committed to being objective, unbiased and honest, presenting all sides of the argument.
This article includes scientific references in brackets, which are clickable links to research papers from reputable academic organizations.

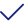
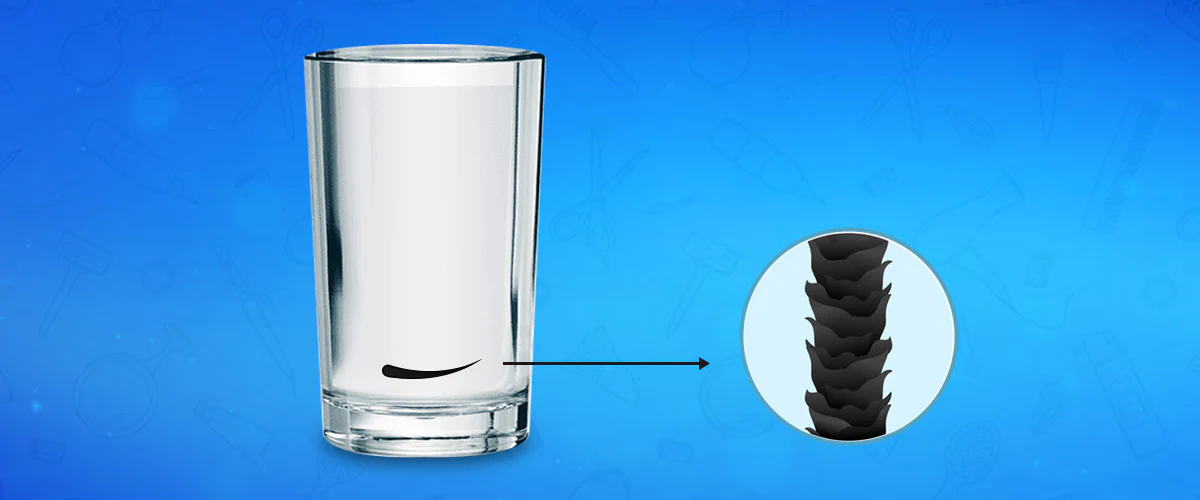
Alopecia areata is a condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and attacks hair follicles resulting in hair loss. It can affect parts of the body including the scalp and face. Importantly it's not contagious.
Alopecia areata can impact individuals of any gender or age. However there are some patterns regarding its prevalence.
Gender: While both men and women can experience alopecia areata it appears to be more common, in men affecting approximately twice as many men as women.
Age: Although this condition can emerge at any age it often develops during childhood or early adulthood. The highest occurrence rates tend to be between the ages of 20 and 40. Nonetheless adults and even seniors may also be affected.
It's essential to keep in mind that these observations represent trends and that alopecia areata can occur at any stage of a persons life.
What are the Main Causes of Alopecia Areata?
The precise cause of alopecia areata remains unknown. However, researchers believe that a combination of factors may contribute to its development.
1. Genetics:
There seems to be a influence as individuals with family members experiencing this condition have a higher likelihood of developing it themselves. Certain genes have been identified as involved in the systems attack, on hair follicles.
2. Autoimmunity:
Alopecia areata falls under the category of diseases, which means that the immune system mistakenly attacks tissues specifically the hair follicles. As a result inflammation occurs and hair loss becomes evident.
3. Triggers from the Environment:
There are factors that could potentially trigger or worsen this condition, such, as;
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress may act as a trigger for some individuals with alopecia areata.
- Illness: Infections or other illnesses can sometimes precede the onset of this condition.
- Chemical Exposure: While uncommon exposure to chemicals or harsh products may contribute to hair loss.
- Psychological Factors: The psychological impact of hair loss can be significant. In some cases can worsen the condition itself.
It's important to note that these factors mentioned above are contributors to alopecia areata and the causes can vary from person to person. Ongoing research aims to gain an understanding of the diseases mechanisms and potential future treatments.
How to Identify the Symptoms of Alopecia Areata?
- The primary symptom indicating alopecia areata is hair loss. These patches typically appear on the scalp but may occur anywhere on the body like eyebrows, eyelashes, beard area or limbs. They start small and round, in shape often resembling the size of a coin.
- The affected areas may appear smooth. Could have a redness or inflammation, at the edges.
- These patches can grow in size. Merge with patches resulting in larger areas of hair loss.
Here are some other possible signs and symptoms commonly associated with alopecia areata.
- Itching or burning sensations in the area where hair loss is about to occur.
- Whitening of hairs within the area.
- Changes in nails, such as pits, dents or brittleness.
- Loss of eyelashes or eyebrows which can cause irritation to the eyes.
It's important to note that not everyone experiencing Alopecia Areata will have all these symptoms. The extent and pattern of hair loss can vary significantly from person to person. If you're concerned about patchy hair loss it's advisable to consult a doctor or dermatologist for a diagnosis and personalized guidance.
Here are some additional points worth keeping in mind;
- Alopecia areata is not contagious.
- It typically does not cause pain.
- While there is no cure available various treatments exist that can help stimulate hair growth and slow down further hair loss.
Alopecia Areata Cure and Treatment:
Regrettably there is yet no known cure, for alopecia areata. There are treatment options to help with hair growth slow down hair loss and manage the condition.
These include
1. Topical Medications:
- Corticosteroids: These creams or ointments are often the treatment choice. They reduce inflammation suppress the systems attack, on hair follicles and can stimulate regrowth.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This topical solution is commonly used for female pattern baldness. Can also be beneficial in some cases of alopecia areata. It promotes hair growth. Thickens existing hair.
- Anthralin: This cream stimulates the system. May be effective for mild to moderate alopecia areata.
2. Injections:
Injecting corticosteroids directly into affected areas can be more effective than using corticosteroids for targeted hair regrowth.
3. Phototherapy:
Ultraviolet (UV) Light Therapy: Exposure to wavelengths of UV light can suppress the system and encourage hair growth.
4. Medications:
- JAK Inhibitors: Newer medications like baricitinib and ritlecitinib target the immune system pathways involved in alopecia areata leading to hair regrowth. However they do have side effects. May not be suitable, for everyone.
These treatment options offer ways to address Alopecia Areata while considering circumstances and potential risks associated with each method.
- Other Medications that Suppress the System: These drugs, such, as cyclosporine and methotrexate are typically used in cases of alopecia areata because they have powerful side effects.
5. Alternative and Complementary Therapies:
Although their scientific efficacy is not proven some individuals report finding relief through therapies like acupuncture, yoga and stress management techniques.
The choice of treatment depends on factors including the extent of hair loss, age, overall health and personal preferences. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist or a specialist in hair loss for a diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
Remember that the effectiveness of treatments can vary from person to person. It's important to be patient since hair regrowth usually takes time with any form of treatment.
Also Read the Articles:
Disclaimer: The information provided on this page is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any questions or concerns about your health, please talk to a healthcare professional.

 Evidence Based
Evidence Based






Leave a comment